Dedicated egress IP using Advanced Networking in AEMaaCS
Configuring Advanced Networking
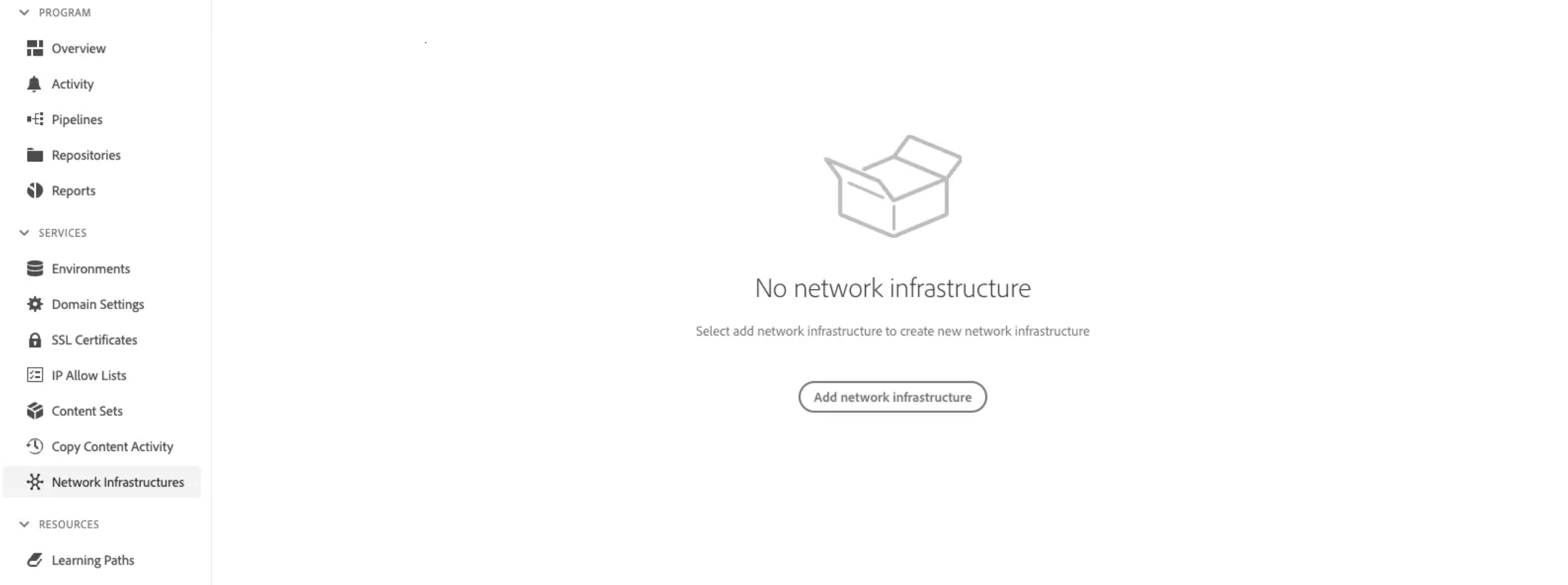
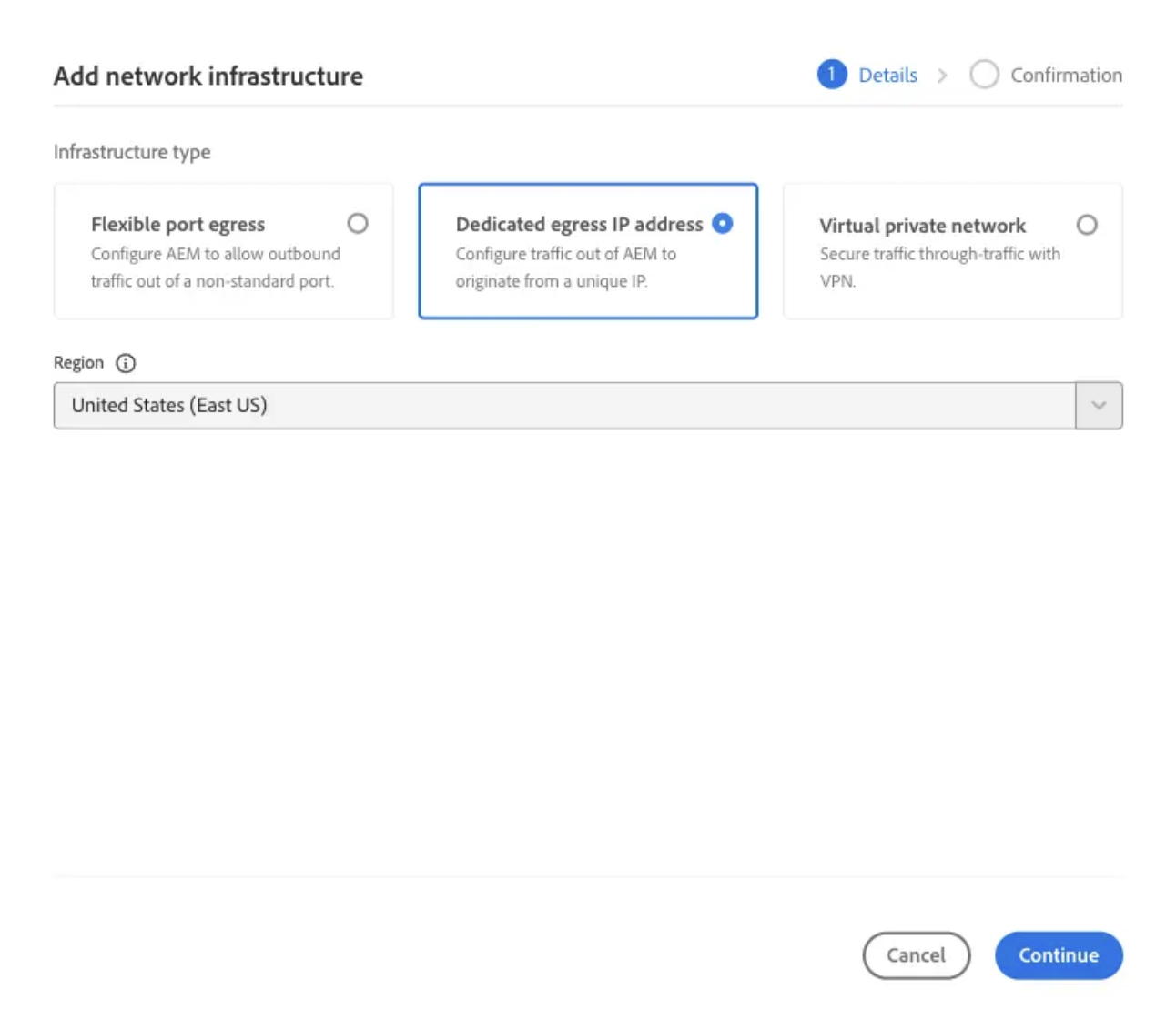
dig command from the command line. Note that the same dedicated egress IP address is shared by all environments in the program, and applies to both Author and Publish services.dig +short p{programId}.external.adobeaemcloud.comEnabling Dedicated Egress IP
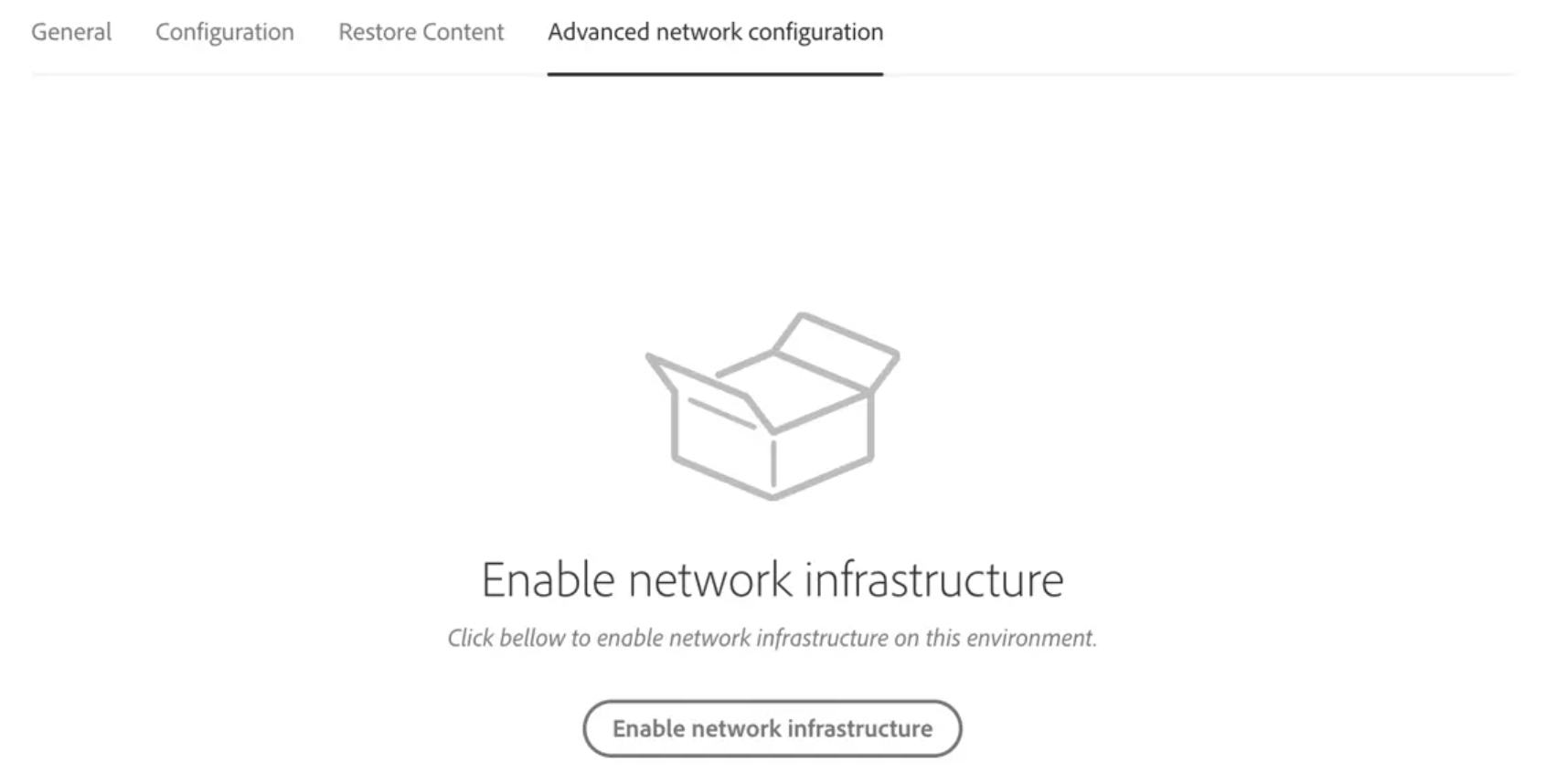
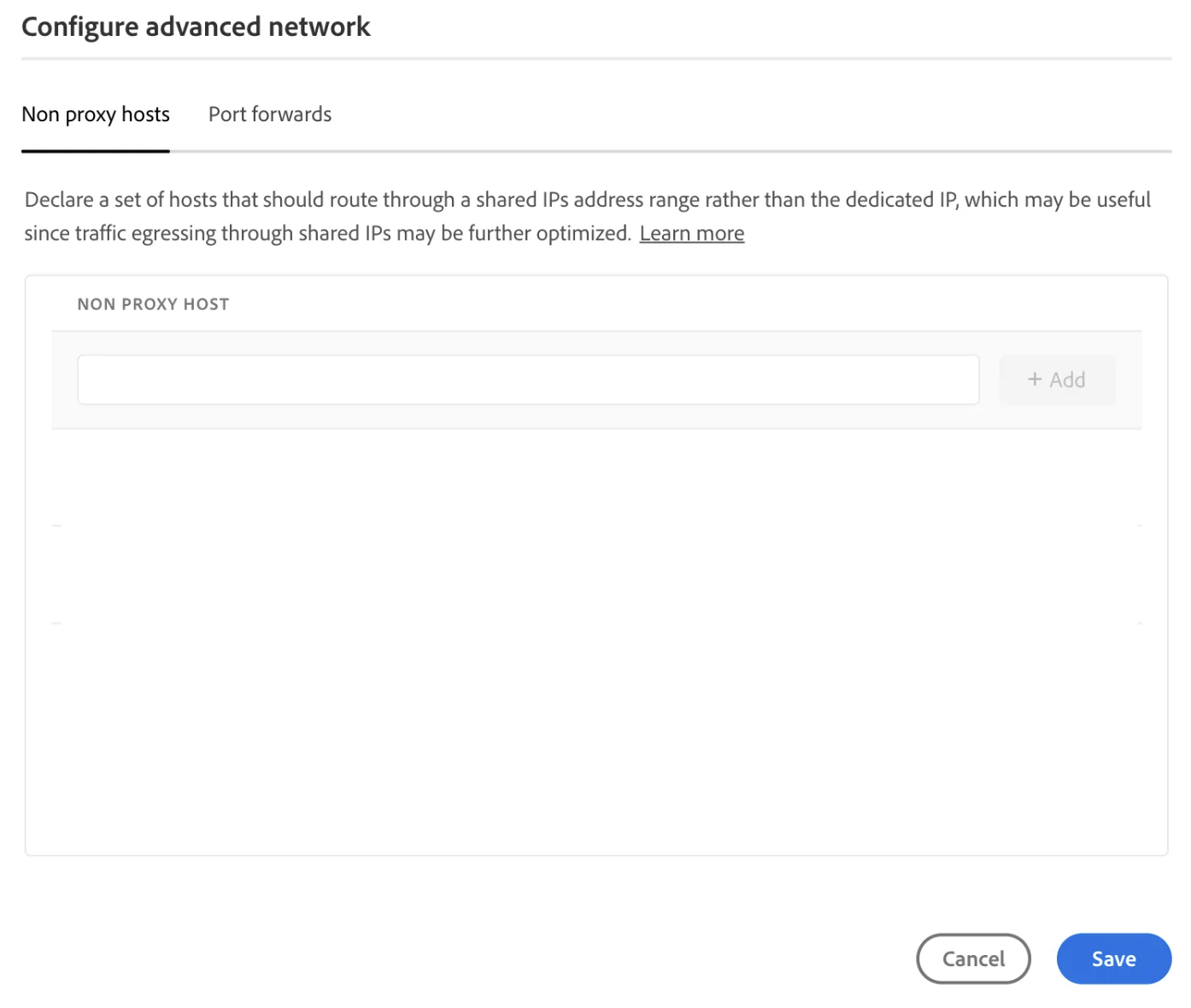
Usage in AEM Backend
HttpClientBuilder, require explicit configuration to use system properties from egress IP settings. Otherwise, they may continue to use the shared IP when sending requests to the client.RestClientService.java
try (CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create()
.setDefaultRequestConfig(getRequestConfig())
.useSystemProperties()
.build()) {
// Implementation goes here
}dig command, you can now whitelist it in your firewall. Once your required changes are deployed to the cloud environment, you should be able to connect to APIs that are hosted behind the firewall.